Amplicon sequencing (AS) technique consists in sequencing the products from multiple PCRs (amplicons). Where a single amplicon is the set of DNA sequences obtained in each individual PCR.
Before the arrival of high-throughput sequencing technologies, PCR products were Sanger sequenced individually. But Sanger sequencing is only able to resolve one DNA sequence (allele) per sample, or as maximum a mix of 2 sequences differing only in one nucleotide (usually heterozygous alleles):
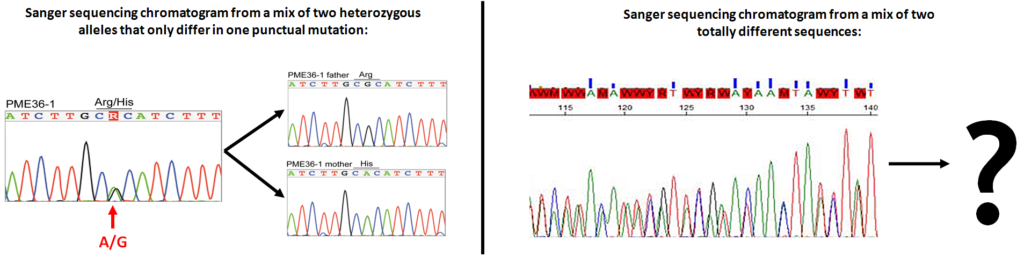
Sanger sequencing limitations
The solution to the previous limitation was bacterial cloning and further isolation, amplification and sequencing of individual clones. Nevertheless, bacterial cloning is a time-consuming approach that is only feasible with few dozens of sequences.
Bacterial cloning to Sanger sequence clones individually
Fortunately, high-throughput sequencing techniques (HTS) also called next-generation sequencing (NGS) are able to sequence millions of sequences with individual resolution. And the combination of amplicon sequencing with NGS allows us to genotype hundreds/thousands of samples in a single experiment.
The only requirement to carry out such kind of experiment is to include different DNA tags to identify the individuals/samples in the experiment. A DNA tag is a short and unique sequence of nucleotides (ex. ACGGTA) that is attached to the 5′ end of any PCR primer or ligated after individual PCR. Each tag should be different for each sample/individual to analyze to be able to classify the sequences or reads from each individual PCR (amplicon) (Binladen et al. 2007; Meyer et al. 2007).
High-throughput amplicon sequencing schema
Again, NGS has other intrinsic problems: sequenced fragments are shorter than in Sanger and sequencing errors are more frequent. Random sequencing errors can be corrected by increasing the depth/coverage: reading more times the same sequence. And longer sequences can be split in shorter fragments and assembled together later by computer.
In the following link you can watch a video explaining the amplicon sequencing process using NGS:
http://www.jove.com/video/51709/next-generation-sequencing-of-16s-ribosomal-rna-gene-amplicons
Basically there are 4 basic steps in an NGS Amplicon Sequencing analysis:
- Experimental design of the primer sequences to amplify the desired gene regions (markers) and of the DNA tags to use to identify samples or individuals.
- PCR amplification of the markers, usually an individual PCR per sample.
- NGS sequencing of the amplification products. The most commonly used techniques are: Illumina, Ion Torrent and 454, also Pac Bio is increasing in importance as its error rate decreases.
- Bioinformatic analysis of the sequencing data. The analysis should consists in: classification of reads into amplicons, sequencing error correction, filtering of spurious and contaminant reads, and final displaying of results in a human readable way, ex. an Excel sheet.
Amplicon Sequencing 4 steps workflow
